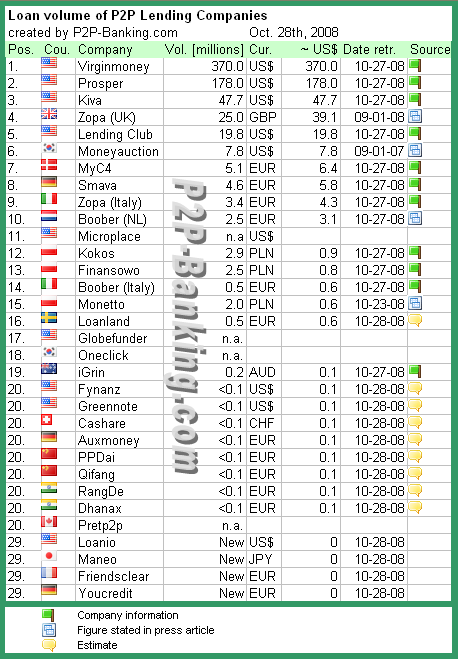
As the end of 2008 approaches here is a look back on the highlights of peer to peer lending news in 2008:
- February: Gartner predicts that by 2010 social lending captures 10% market share; p2p lending in Poland takes off; IOUcentral launches in Canada – only to be suspended by regulator a week later
- April: Lendingclub enters quiet period for SEC registration; Cashare launches p2p lending service in Switzerland; Prosper goes national with 36 percent max. interest rate – partnering with WebBank; Zopa UK reshapes markets – concentrates on 36 and 60 months loan terms
- May: MyC4 has new interface and shifts currency risks to lenders
- August: Zopa UK launches young market; Maneo launches p2p lending services in Japan
- September: Kiva repayments are now immediately available for reinvestment; Zopa grows in Italy – has secondary market
- October: Loanio launches in the US; Friendsclear launches in France; Smava raises more venture capital; Zopa US closes; Veecus launces p2p microfinance; Lending club comes out of quiet period and introduces secondary market note trading platform; Prosper enters quiet period for SEC registration; Kiva wins grant; more than 685M US$ p2p lending volume; two funds will invest more than 2M Euro in Africa through MyC4
- November: 50 million US$ Kiva loans reached; Comunitae gets funding; SEC orders Prosper to cease and desist; Loanio suspends operations
- December: Class action lawsuit and other legal troubles challenge Prosper

 A possible argument against classifying MyC4 and Kiva as p2p lending companies is the fact that they use local microfinance institutions as intermediaries acting between lender and borrower and charging fees. That is true, but several other p2p lending services (e.g. Prosper, Lending Club and Smava) use banks as intermediaries (for legal reasons).
A possible argument against classifying MyC4 and Kiva as p2p lending companies is the fact that they use local microfinance institutions as intermediaries acting between lender and borrower and charging fees. That is true, but several other p2p lending services (e.g. Prosper, Lending Club and Smava) use banks as intermediaries (for legal reasons).