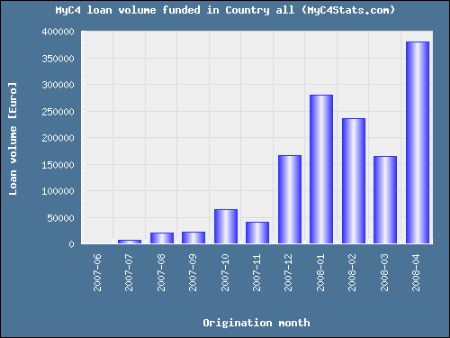
Today MyC4 presents itself in an all new shiny layout. On MyC4 lenders can give loans to small businesses in Africa. Unlike at Kiva, lenders at MyC4 earn interest. So far 1.8 million Euros (approx. 1.2 million US$) have been invested in loans and there are no defaults yet – only several late payments. With the new release …
… three key elements have been prioritized on the new website; usability, design and communication. We have made it easier to understand what MyC4 is all about, how to join, how to upload money, how to find a Business, which fits your criteria and lastly how you invest and re-invest.
According to MyC4 the changes in today's release are:
- The look of MyC4.com has been updated
- Improved navigation making it easier to find your way around via a top menu and a left hand menu with sub-levels
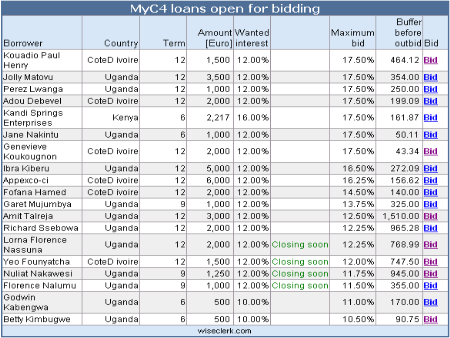
- “Opportunity” changed to “Business” – to access the overview of Businesses, click on “INVEST” in the top menu
- MyCredits is now changed to EURO (€)
- The Investor now carries the Currency Risk
- Withholding tax
I also noticed that MyC4 is no longer marked as "beta".
The handling of currency risk is a major change. The announcement email says:
At MyC4 we want to offer a sustainable and easy to understand solution for the African Businesses. The currency Risk has until now been carried by the African Business, but this has uncertainty for their loan conditions.
To ensure that MyC4 and the African Businesses are sustainable in the long run a new model for the Currency Risk has been developed. We now transfer the Currency Risk to the Investor, which has to be covered by the size of the interest rate you demand.
As a consequence please be aware that going forward there is a Currency Risk on your new investment when investing in some African countries. MyC4 cannot advise on the daily currency development, but based on the last 3 years currency fluctuation we suggest as a guideline that your add the following percentages to your normal wanted interest rate to cover for the potential Currency Risk;
Uganda 6%
Kenya 2%
Côte d’Ivoire 0%This means that if you where planning to Bid on a Business in Kenya with an interest of 8% in mind you now add the 2% – so you Bid 10%, but will properly get 8% depending on the currency fluctuation over the period of the loan.
Screenshot of MyC4 in new design